How Postbid Works in Prebid: A Practical Guide for Publishers
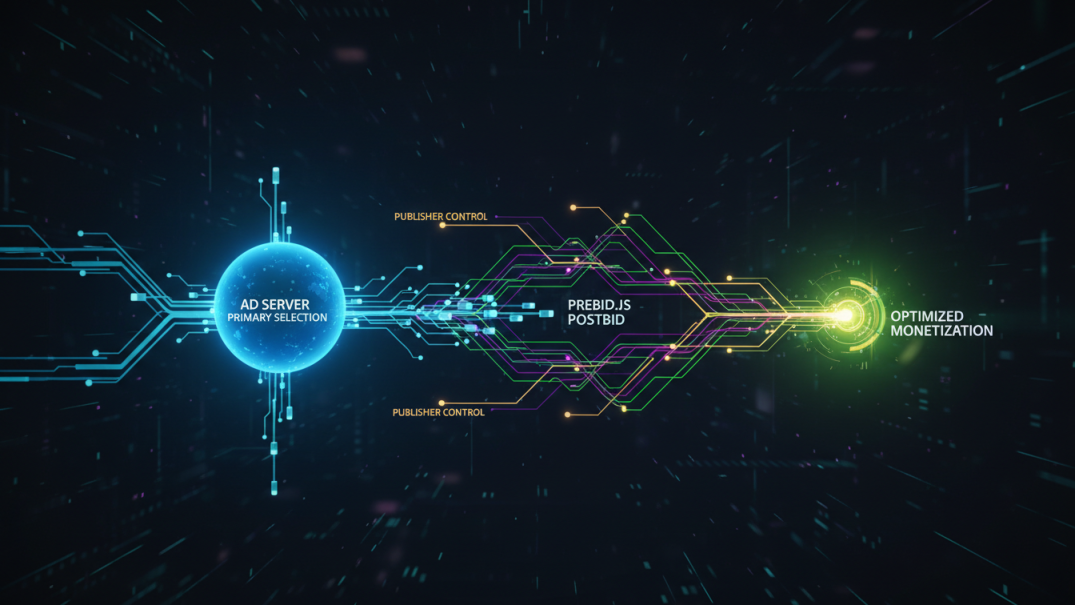
Managing header bidding can become complex, especially when it comes to optimizing monetization after your ad server has made the primary ad selection. Postbid provides an alternative approach—one that leverages Prebid.js in a way that puts publishers in full control, even after the initial ad server auction.
For publishers and ad operations teams, understanding the technical flow and implications of Postbid is key to troubleshooting, maximizing revenue, and ensuring a smooth integration within your existing stack. This guide breaks down how Postbid works, why it matters, and what you need to consider before moving beyond pre-auction header bidding.
Understanding Postbid: What Sets It Apart?
Postbid is a method of running header bidding after your ad server (such as Google Ad Manager) chooses a line item. Unlike standard header bidding, where Prebid.js runs on the page and feeds bids into the server, Postbid delivers a creative—often a third-party tag—that loads Prebid.js only if that ad slot is chosen. This approach gives publishers a fallback opportunity to run their own auction in specific ad units, adding flexibility to their setup.
When Should You Use Postbid?
Postbid is well-suited for scenarios where:
– You want to fill otherwise remnant inventory after the ad server auction.
– You wish to test direct demand or custom auctions in specific placements.
– Your tech stack or policies restrict running full header bidding on-page for all impressions.
It is not a replacement for standard header bidding, but a complement for maximizing value in lower-priority ad opportunities.
Technical Flow: How Postbid Works with Prebid.js
Implementing Postbid means serving a creative (often via an
